Everything You Need to Know About SMPS: Selection, Efficiency, and Industrial Applications
In today's fast-paced world of industrial automation, data systems, and smart energy solutions, ensuring reliable power delivery is non-negotiable. That's where Switching Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) come into play. Known for their compact design, high efficiency, and adaptability across various environments, SMPS units have become the go-to power solution for everything from factory equipment to intelligent lighting. This article explores the key questions professionals often ask when evaluating SMPS for real-world applications—covering types, selection criteria, energy efficiency, and the importance of choosing the right manufacturer.
Table of Contents
What Is SMPS and Why Is It Widely Used in Modern Electronics?
How Do Different Types of SMPS Meet Industry-Specific Needs?
What Are the Key Selection Criteria for an SMPS?
How Does SMPS Contribute to Energy Efficiency and Sustainability?
Why Is It Crucial to Source SMPS from a Reliable Manufacturer?
What Is SMPS and Why Is It Widely Used in Modern Electronics?
Overview of SMPS Functionality
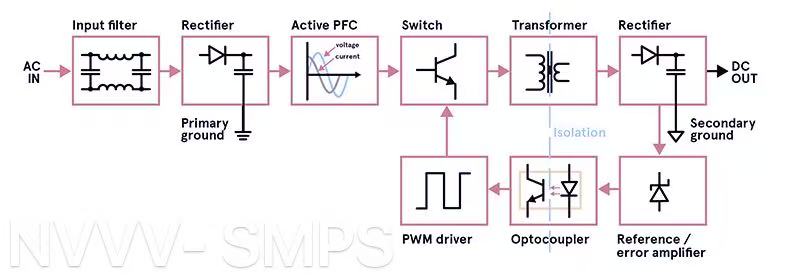
A Switching Mode Power Supply (SMPS) is an essential component in modern power electronics, converting electrical energy from one form to another with minimal loss. It achieves this by rapidly switching transistors on and off at high frequencies—typically tens or hundreds of kilohertz—allowing energy to be stored and released in transformers or inductors more efficiently than in linear power supplies. This results in not only energy savings but also compact design and reduced heat dissipation. Unlike linear power supplies, which rely on bulky transformers and dissipate excess energy as heat, SMPS offers a smarter and more compact approach for power conversion.
Efficiency and Compactness
Efficiency is one of the most compelling reasons why engineers prefer SMPS in both consumer and industrial systems. While linear supplies may offer around 50–60% efficiency, SMPS units can reach efficiencies upwards of 90–95%, particularly when using advanced control techniques like pulse-width modulation (PWM) or resonant switching. This high efficiency means less heat is generated, reducing the need for large heat sinks or forced cooling. In space-constrained environments—such as control cabinets, LED lighting systems, and telecom enclosures—this is a significant advantage, allowing for more compact installations and lower overall system cost.
Universal Input Compatibility
Modern SMPS designs often feature wide-range universal AC input, typically from 85V to 265V, and are also compatible with DC inputs ranging from 100V to 370V. This makes them suitable for global use without the need for different models for different regions. This is especially useful for multinational OEMs and integrators who require standardized components that comply with various electrical grids across Europe, the Middle East, and beyond. Additionally, built-in active power factor correction (PFC) ensures compliance with international standards while improving input current quality.
Additional Benefits in Real-World Systems
Weight Reduction: Thanks to high-frequency transformers, SMPS systems are much lighter than equivalent linear power supplies.
Better Load Regulation: Fast feedback loops allow for more stable voltage and current outputs under dynamic load changes.
Multiple Outputs: Many SMPS units offer dual or triple output rails, simplifying design for systems that require both 5V and 12V outputs, for example.
How Do Different Types of SMPS Meet Industry-Specific Needs?
Types of SMPS Based on Topology
SMPS can be categorized by their circuit topologies, each offering distinct benefits based on voltage conversion needs and power ratings.
A buck converter steps down voltage and is ideal for powering logic circuits and embedded controllers.
A boost converter increases voltage, useful in battery-powered devices requiring stable higher outputs.
The buck-boost design can invert or regulate voltage above or below the input, ideal for unpredictable power conditions.
Flyback converters, commonly used in compact devices and low-power applications, offer isolation and cost-effectiveness.
Forward and full-bridge converters are favored in high-power applications like industrial drives and server power systems.
Each topology addresses specific challenges: voltage polarity, load regulation, isolation, or efficiency. For instance, flyback SMPS with built-in galvanic isolation are perfect for powering control circuits in HVAC systems or instrumentation where safety barriers are needed.
Application-Based Classification
Different industries demand specific SMPS characteristics. Here's how these variations align with sector-specific needs:
Industrial Automation: Requires robust power supplies with reinforced isolation, DIN-rail mounting, and wide temperature tolerance. These units often include surge protection, conformal coatings for moisture resistance, and hot-swap capabilities.
Medical Equipment: Demands ultra-low noise output, IEC 60601 certification, and creepage/clearance compliance. SMPS used here often include redundancy, EMI shielding, and Class II insulation to meet stringent safety standards.
Telecom & Data Centers: Rely on redundant SMPS with hot-swappable modules, remote monitoring, and N+1 backup configurations. High power density and 48V output standards are common in these environments.
LED and Display Systems: Use dimmable and PFC-compliant SMPS that integrate well with lighting control systems. These are often fanless and designed for silent operation in indoor environments like signage or architectural lighting.
Built-In Protection Features
No matter the application, advanced switched mode power supplies products include integrated protections such as:
Over-voltage protection (OVP)
Short-circuit protection (SCP)
Thermal shutdown
Input surge suppression
These ensure the longevity and safe operation of downstream devices, especially in sensitive or mission-critical settings.
Future-Ready Design Considerations
With increasing focus on IoT integration and remote diagnostics, many SMPS units now come with communication interfaces like RS485, CANbus, or Modbus, allowing centralized monitoring and predictive maintenance in large systems like smart factories or renewable energy platforms.
What Are the Key Selection Criteria for an SMPS?
Input and Output Voltage Compatibility
When selecting a Switch Mode Power Supply, the first step is to evaluate the input and output voltage range. Most SMPS products support a universal AC input (85–265V), but if your system operates in a controlled environment—like a DC-powered solar application—you might need models supporting DC input ranges like 100–370V.
On the output side, ensure the voltage aligns with your device requirements. 24V output is common in industrial sensors and relays, while 5V or 12V outputs suit embedded electronics and communication modules. A mismatch could lead to underperformance or even damage.
Power Rating and Load Consideration
A common pitfall is underestimating your power needs. To avoid overloading the SMPS, calculate the total current draw of all connected components and then multiply by the output voltage to determine the required wattage.
Tip: Always add a 20–30% buffer above your estimated power load to account for startup surges or future expansion.
For example, if your system requires 3A at 24V:
24V × 3A = 72W → Add 30% = ~94W ⇒ Choose a 100W SMPS
Thermal Management and Cooling
Heat is the silent killer of power supplies. Depending on your environment—open rack, enclosed panel, or ventilated space—you should consider how the SMPS handles heat.
Fanless SMPS (convection cooling) are ideal for quiet or sealed environments but may require derating.
Fan-cooled SMPS offer better heat dissipation but can introduce noise and require more maintenance.
Manufacturers usually provide derating curves—graphs that show how power output must be reduced at elevated temperatures. Always refer to this data during design.
Form Factor and Mounting Options
The physical dimensions and mounting style of your SMPS also matter:
DIN-rail models for easy installation in control cabinets.
Open-frame designs for integration into compact devices.
Enclosed models for standalone or field installations with dust/humidity protection.
Check for mounting hole positions, clearance needs, and cooling airflow paths before finalizing your choice.
Certifications and Compliance
Depending on your region or export market, the SMPS must meet specific certifications such as:
CE (Europe)
UL or cUL (North America)
RoHS/REACH (Environmental)
EN/IEC 61000 (EMI compliance)
These standards ensure your device passes factory audits and customs clearances without issue, especially critical for OEMs exporting to multiple regions.
Example Checklist for SMPS Selection
Input voltage range (AC/DC)
Output voltage and current
Total wattage with safety margin
Thermal and cooling needs
Mounting type (DIN, screw, enclosure)
Compliance (CE, UL, RoHS, EMC)
Built-in protections (OVP, OCP, SCP)
How Does SMPS Contribute to Energy Efficiency and Sustainability?
High Efficiency = Lower Energy Bills
Switching Power Supplies are celebrated for their exceptionally high conversion efficiency, often reaching 90–95%, especially when using modern control techniques like soft switching or zero-voltage switching (ZVS). This translates directly to reduced electricity costs, which becomes particularly impactful in high-consumption environments such as manufacturing plants, automation systems, and smart buildings.
The formula is simple: less energy lost as heat → less cooling required → lower overall operating costs. Over time, this not only benefits your company's bottom line but also contributes to broader carbon reduction goals.
Minimal Standby Power Consumption
Modern SMPS designs also address phantom loads—the energy consumed while a device is idle. Many power supply models now feature standby power consumption below 0.5W, aligning with ErP Lot 6 and Lot 7 energy directives in Europe. This makes them suitable for energy-conscious sectors, such as green building development or solar-powered systems where every watt matters.
Built-in Power Factor Correction (PFC)
Poor power factor can lead to inefficiencies in industrial electrical networks. SMPS with active PFC circuitry help align voltage and current phases, reducing harmonic distortion and improving grid load efficiency. This is especially useful in applications with multiple power supplies operating simultaneously, such as data centers or production lines.
Sustainable Product Design
Sustainability in SMPS doesn't stop at efficiency. Many high-quality units are now designed with:
RoHS-compliant materials (no lead, cadmium, or mercury)
Low-noise components for minimal EMI impact
Recyclable enclosures made of aluminum or halogen-free plastics
These design principles not only support corporate sustainability goals, but also ensure smooth market entry into countries with stringent environmental regulations like Germany, France, and UAE.
Extending the Lifespan of Connected Equipment
An underrated benefit of high-performance SMPS is their ability to stabilize voltage and reduce electrical stress on sensitive equipment. Inconsistent power—especially in regions with unstable grids—can degrade the lifespan of motors, PLCs, or microcontrollers.
By delivering tightly regulated DC output and offering layered protection features (e.g., overvoltage, short-circuit, over-temperature), SMPS serve as an electrical shield for your system, enhancing overall reliability and reducing repair costs.
Eco-Conscious Maintenance and Monitoring
More advanced SMPS models now support smart interfaces like Modbus RTU, RS485, or IoT dashboards for remote monitoring. These tools help facilities detect abnormal power usage early, optimize energy distribution, and schedule proactive maintenance—key strategies in minimizing waste and downtime.
Why Is It Crucial to Source SMPS from a Reliable Manufacturer?
Consistent Quality and Global Certifications
The performance of an SMPS is only as good as its internal components and manufacturing standards. A reputable manufacturer ensures high-grade capacitors, robust transformers, and precision IC controllers are used in every unit. This results in consistent performance across batches and minimal failure rates in the field.
Moreover, trusted brands subject their power supplies to rigorous third-party testing, earning certifications such as:
CE (including CE-LVD and CE-EMC) for compliance with European Union safety and electromagnetic compatibility standards
UKCA (UK Conformity Assessed) covering both Low Voltage and EMC for seamless deployment in the United Kingdom
RoHS confirming that products are free from hazardous substances like lead or cadmium
CCC (China Compulsory Certification) for quality assurance in China
ISO9001, ensuring a global standard in quality management systems
IP67 ratings on selected models for dustproof and waterproof applications
These certifications ensure compatibility and safety across a wide range of applications and geographies, while also streamlining customs clearance and project approval processes—particularly important for cross-border projects or government tenders.
Advanced Features and Customization Options
Well-established manufacturers often go beyond basic power delivery. They integrate advanced features such as:
Remote On/Off control terminals
Digital voltage tuning interfaces
Redundant parallel operation support
Status LEDs or diagnostic signals
Some even offer customized voltage rails, thermal coatings, or tailored mechanical enclosures to fit specific application constraints, especially in aerospace or military projects where every detail counts.
Reliable After-Sales Support and Documentation
Technical support is crucial in industrial settings. A responsible SMPS supplier offers:
Detailed datasheets and 3D drawings
Application notes for EMI reduction or system integration
Firmware updates or configuration tools
In the event of a failure, responsive RMA policies, regional distribution networks, and expert troubleshooting can significantly reduce downtime and project delays.
Reputation and Field Experience
Established manufacturers have a history of supporting large-scale industrial projects, giving them unique insights into real-world performance and reliability challenges. Their feedback loops with OEM clients help drive continuous product improvement.
Case in Point: NVVV SMPS Solutions
Among trusted names in the field, NVVV stands out as a reliable supplier of industrial-grade SMPS products. Their offerings include:
Wide input range (90–264VAC) compatible with global grids
Output options from 5V to 48V with models up to 1000W
Multiple form factors: enclosed, open-frame, and DIN-rail mounted
Built-in protection features such as OVP, OCP, SCP, and thermal shutdown
NVVV's SMPS units are backed by certifications such as CE, UKCA, RoHS, ISO9001, 3C, and even IP67 ratings on selected models. These credentials make them ready for diverse installations—from clean indoor automation panels to rugged outdoor lighting systems—ensuring stable, compliant, and long-lasting power delivery.
Conclusion
Choosing the right SMPS is more than a technical decision—it's a strategic investment in your system's long-term reliability and efficiency. From understanding the different topologies and applications to assessing certifications and sustainability, each aspect plays a crucial role in performance. Brands like NVVV, with their extensive range of certified, industrial-grade SMPS units, provide not only the power you need but also the peace of mind that comes with global compliance and quality assurance. Whether you're upgrading existing infrastructure or building from the ground up, a dependable SMPS partner ensures your power system is built to last.