How to Select the Right Switching Mode Power Supply for Industrial Use
In today’s interconnected world, where efficiency and precision matter more than ever, switching mode power supplies (SMPS) have become the backbone of countless industrial and commercial systems. Whether it’s in smart grid applications, manufacturing machinery, or renewable energy setups, SMPS units deliver reliable power conversion with minimal loss and optimal control.
But why are more system designers in Europe and the Middle East switching to SMPS? What do you need to consider when choosing one for your application? In this article, we’ll dive into these questions and more—giving you a practical, easy-to-understand guide that reflects local industry needs and expectations.
Table of Contents
Why Are Switching Mode Power Supplies Preferred in Industrial Applications Today?
How Does a Switching Mode Power Supply Work and What Sets It Apart?
Where Are Switching Mode Power Supplies Used Across Europe and the Middle East?
What Factors Should You Consider When Choosing a Switching Mode Power Supply?
What Are the Emerging Trends in Switching Mode Power Supply Technology?
1. Why Are Switching Mode Power Supplies Preferred in Industrial Applications Today?
Switching mode power supplies have rapidly overtaken traditional linear power supplies in industrial environments, and for good reasons. At the heart of this shift is the demand for higher energy efficiency, smaller footprints, and greater design flexibility—needs that are especially pronounced in European and Middle Eastern industries where space optimization and long-term operational savings are top priorities.
Efficiency Gains
Unlike linear models, SMPS devices regulate voltage by quickly switching on and off, using high-frequency signals to convert power with minimal heat loss. This translates to conversion efficiencies exceeding 85%, which significantly reduces electricity costs in high-volume operations.
Compact and Lightweight Design
In sectors like telecom infrastructure, water pumping systems, or automated lighting solutions, cabinet space is often limited. SMPS units offer compact housing, making it easier to integrate them into both new and retrofit systems without additional infrastructure costs.
Voltage Versatility
SMPS systems are designed to handle a wide input voltage range—a crucial feature in regions with fluctuating power grids or hybrid energy setups combining solar, grid, and generator sources. This flexibility allows the same unit to be deployed in various settings across Europe and the Middle East without major modifications.
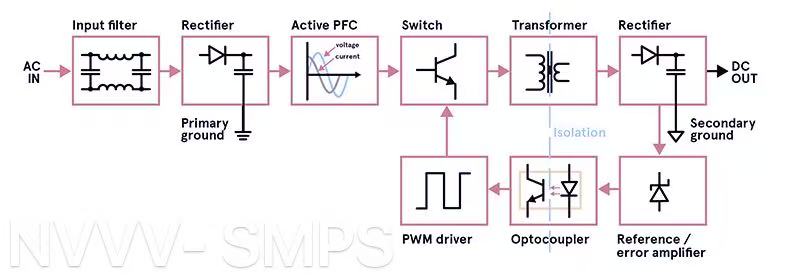
2. How Does a Switching Mode Power Supply Work and What Sets It Apart?
Understanding how a switching mode power supply (SMPS) functions is key to recognizing its advantages over conventional alternatives. While the underlying process involves some complex electronics, the core idea is quite straightforward: SMPS converts electrical energy efficiently by rapidly switching components on and off, instead of dissipating excess voltage like a linear power supply.
Core Operating Principle
At its simplest, an SMPS takes incoming electrical power—either AC or DC—and converts it to the desired output voltage through a combination of high-frequency switching transistors, transformers, and filters. This process includes four main stages:
Rectification – If the input is AC, it’s first converted to DC using a rectifier.
Switching – A high-speed switch (often a MOSFET) chops the DC into high-frequency pulses.
Transformation – The pulses pass through a transformer, which adjusts the voltage up or down as needed.
Filtering and Regulation – Finally, capacitors and inductors smooth the output, and a feedback loop keeps voltage levels stable under varying loads.
This technique allows SMPS units to respond dynamically to changes in load and input voltage—something linear power supplies cannot do as efficiently.
High-Frequency Advantage
The use of high-frequency switching (typically 20 kHz to several MHz) enables the use of smaller transformers and components, significantly reducing the overall size and weight. For installations where equipment space is limited—such as compact control panels or mobile systems—this is a major benefit.
Reduced Heat, Improved Lifespan
In Europe and the Middle East, where ambient temperatures can vary widely—from freezing winters to extreme summer heat—equipment that generates less heat is highly valued. Since SMPS operates with high efficiency, less energy is lost as heat. This reduces the need for large heat sinks or active cooling, and improves the longevity of both the power supply and surrounding equipment.
Noise and EMI Considerations
One concern often raised is the electromagnetic interference (EMI) that SMPS can generate due to rapid switching. However, modern designs use shielding and filtering techniques that meet stringent European EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) directives. Many manufacturers now design their SMPS units specifically to comply with both CE and RoHS standards.
3. Where Are Switching Mode Power Supplies Used Across Europe and the Middle East?
Switching power supplies are not limited to one industry—they’re an essential part of numerous applications across Europe and the Middle East, where demand for high-efficiency, compact power conversion is on the rise. Whether it’s for infrastructure, automation, or energy innovation, SMPS systems have become a foundation in sectors that value both performance and reliability.
Industrial Automation and Machinery
In countries like Germany, Italy, Turkey, and the UAE, industrial automation is a key driver of economic growth. SMPS units are used to power programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, actuators, and motor controllers on production lines. Because they offer consistent voltage output and can handle variable loads, they’re ideal for automation systems that demand uninterrupted operation.
In these settings, SMPS units are often integrated into DIN rail-mounted enclosures, which is a standard form factor in European electrical panels. Compact and standardized, they reduce setup time and simplify maintenance.
Renewable Energy and Smart Grids
With solar and wind energy projects booming across Spain, Greece, Egypt, and Jordan, the role of SMPS in renewable infrastructure is expanding. For example, they’re used to power the control systems of solar inverters and battery management systems. Their ability to regulate voltage precisely helps optimize energy conversion and storage.
Moreover, many smart grid installations in Europe use SMPS-powered telemetry systems for real-time monitoring, helping utilities manage electricity more efficiently.
Water Management and Pumping Systems
In Middle Eastern regions where water scarcity drives innovation, SMPS units are used in automatic pump controllers, irrigation systems, and desalination equipment. These applications require stable power for sensor arrays and automated valves. Since grid stability can be inconsistent in some rural or remote areas, the wide input voltage range and surge protection of SMPS units offer clear benefits.
Telecom and Data Centers
Data traffic is growing rapidly in hubs like Frankfurt, Dubai, and Riyadh. Telecom towers and data centers rely heavily on DC power systems, where SMPS is used for backup power, base station equipment, and network switches. Their compact size, high efficiency, and low heat output make them ideal for dense server environments and tower enclosures.
Transportation and Public Infrastructure
European railway systems and Middle Eastern airport control systems often include SMPS in their electrical cabinets. These units power onboard lighting, control circuits, and safety systems. Their ability to withstand harsh environments (e.g., vibrations, voltage spikes) makes them dependable even in mission-critical transport setups.
4. What Factors Should You Consider When Choosing a Switching Mode Power Supply?
Selecting the right switched mode power supply (SMPS) is not just about matching voltage and current ratings—it’s about ensuring the entire system performs reliably under real-world conditions. In Europe and the Middle East, where operational environments and regulatory standards can vary significantly, these considerations become even more critical.
Here’s a detailed look at what to evaluate before making your selection.
1. Input Voltage Range Compatibility
One of the most essential criteria is whether the SMPS can handle the local power grid conditions. For instance, some areas in the Middle East experience voltage fluctuations or operate on non-standard mains supply. A wide input range (e.g., 85–264VAC or 100–370VDC) ensures that your equipment remains stable even during voltage dips or surges.
In regions where off-grid solar or generator power is used, SMPS devices with dual input (AC/DC) compatibility are especially valuable.
2. Load Type and Tolerance
Different applications present different types of electrical loads—resistive, inductive, or capacitive. Motor drives, for example, require inrush current handling; LED lighting requires low ripple output. Choosing an SMPS with the correct overload protection, inrush current limit, and power factor correction (PFC) helps ensure system longevity.
For automation or instrumentation, look for models with low ripple noise and tight regulation to prevent interference with sensitive electronics.
3. Thermal Performance and Ambient Conditions
Will your SMPS be installed in a high-temperature desert environment? Or a cold factory floor in northern Europe? Many users overlook the importance of temperature rating, cooling method (convection vs. fan), and derating curves. These factors determine how well the unit performs at full load across a wide temperature range.
In compact enclosures or sealed environments, passively cooled models (without fans) are preferred for long-term durability.
4. Form Factor and Mounting Options
European electrical panels often use DIN rail mounting, while in Middle Eastern industrial setups, there’s a mix of panel-mount and chassis-mount preferences. Make sure your chosen SMPS supports the physical format needed for your installation.
Compact form factors and modular designs can also reduce cabinet space and ease maintenance.
5. Certifications and Compliance
Especially important in cross-border operations, check for CE marking, RoHS compliance, UL certifications, and local approvals. In the EU, EMC directives and Low Voltage Directives (LVD) must be met. In the Middle East, certifications that align with Gulf Standardization Organization (GSO) requirements or Saudi Product Safety standards (SABER) may be essential for customs clearance.
6. Protection Features
For environments with unstable power or harsh operating conditions, look for features like:
Over-voltage protection (OVP)
Over-temperature protection (OTP)
Short-circuit protection
Surge immunity
These not only protect your power supply but also shield downstream components from damage.
7. Vendor Reliability and Local Support
Finally, while the technical specs matter, so does the availability of support. Many industrial users in Europe and the Middle East value vendors who can offer fast delivery, localized service, and technical consultation. Brands that maintain strong distribution channels and multilingual documentation often win long-term partnerships.
5. What Are the Emerging Trends in Switching Mode Power Supply Technology?
The switch mode power supply (SMPS) market is evolving rapidly—driven by the global push for energy efficiency, smart automation, and renewable integration. Across Europe and the Middle East, these trends are reshaping how companies select, design, and deploy SMPS solutions. Staying updated with these developments is essential for businesses that want to remain competitive, efficient, and compliant.
1. Digital Control and Smart Monitoring
Modern SMPS units are no longer passive power converters—they’re becoming intelligent devices. With embedded microcontrollers and digital signal processors (DSPs), newer models offer real-time performance monitoring, remote configuration, and even self-diagnostics.
This is particularly valuable in smart factories, data centers, and energy management systems. Imagine a power supply that can warn you before it fails, or automatically adjust output based on load conditions or temperature.
In Europe, where Industry 4.0 adoption is high, such smart SMPS features align perfectly with predictive maintenance and connected infrastructure strategies. Meanwhile, in Middle Eastern markets focused on digital infrastructure development, these technologies are being used in utility and telecom systems for greater control and reliability.
2. Wide Bandgap Semiconductors (GaN & SiC)
Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are revolutionizing SMPS design. Compared to traditional silicon-based components, GaN and SiC allow higher switching frequencies with lower power losses, smaller heatsinks, and higher power density.
This leads to:
Smaller footprints
Improved thermal efficiency
Faster response times
Greater power output in the same volume
These semiconductors are gaining traction in EV chargers, telecom base stations, and solar inverters—applications common in both European smart cities and Middle Eastern infrastructure megaprojects.
3. Modular and Hot-Swappable Designs
Flexibility is a rising requirement, especially for data centers, telecom hubs, and field-deployed systems. Modular SMPS systems allow users to scale power capacity up or down based on evolving needs.
Hot-swappable designs, which can be replaced without shutting down the system, reduce downtime and increase operational efficiency. This is a key requirement in 24/7 industrial operations where any delay can lead to significant financial losses.
4. Energy Efficiency Compliance and Eco Design
Environmental responsibility is no longer optional. In the EU, the Ecodesign Directive (2009/125/EC) mandates minimum efficiency levels and standby power limits. Newer SMPS units are designed to meet these stringent energy-saving targets, reducing operating costs and helping businesses achieve their sustainability goals.
In the Middle East, green building initiatives like the Estidama Pearl Rating System (UAE) and Saudi Green Building Forum are encouraging industries to adopt high-efficiency power solutions. SMPS units with efficiency ratings above 90% are now standard for many government and private tenders.
5. Harsh Environment & Ruggedization Trends
For outdoor, marine, or desert-based applications, the demand for rugged SMPS designs is growing. Features like:
Conformal coating
IP65/IP67 protection
Extended temperature operation (-40°C to +85°C)
Vibration and shock resistance
...are becoming increasingly important for military, oil & gas, and transportation projects across the Middle East and Europe.
With so many innovations shaping the SMPS landscape, the question now becomes—who can you rely on for products that combine all these advanced features with proven quality?
Final Thoughts: Future-Ready Power Solutions for Demanding Industries
As industries across Europe and the Middle East continue to digitize, automate, and prioritize sustainability, switching mode power supplies will remain a vital component in every system. From powering precision sensors to driving heavy machinery, the right SMPS enhances efficiency, reliability, and scalability.
Whether you're upgrading an existing setup or building a new system from the ground up, the key lies in selecting a power supply that’s not only technically capable but also designed for your environment, regulatory needs, and long-term goals.
About NVVV
NVVV is a trusted name in the field of power electronics, offering a diverse range of switching mode power supplies engineered for durability, efficiency, and compliance. With a focus on serving industrial and infrastructure clients across global markets—including Europe and the Middle East—NVVV combines innovative design with dependable support, helping businesses power their future with confidence.