Why Switching Mode Power Supplies Are Revolutionizing Modern Industrial Power Needs
Power supply technologies have evolved significantly, but one category stands out as the industry standard across most modern applications—Switching Power Supplies (SMPS). Whether you're managing a data center, automation line, or network control room, the SMPS often plays a behind-the-scenes but critical role in keeping things efficient, compact, and reliable.
Unlike older linear power supplies, switching mode power supplies convert electrical energy more efficiently, reduce heat generation, and adapt seamlessly to various voltage conditions. But that’s only scratching the surface.
In this article, we’ll dive into the reasons why SMPS has become the go-to choice for industrial systems and answer the key questions decision-makers often have when considering power supply upgrades or new installations.
Table of Contents
What Are Switching Mode Power Supplies and How Do They Work?
Why Is SMPS Better Suited for Industrial Environments Than Traditional Power Supplies?
How Do You Choose the Right Switching Mode Power Supply?
What Problems Can SMPS Help Solve in Complex Industrial Systems?
Are There Any Limitations or Challenges with SMPS?
Final Thoughts: Is It Time to Upgrade to SMPS?
What Are Switching Mode Power Supplies and How Do They Work?
A Quick Technical Overview
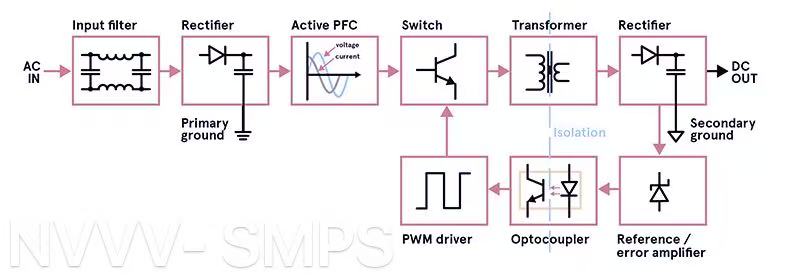
A switching mode power supply (SMPS) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. It uses high-frequency switching transistors and energy storage components like inductors and capacitors to transfer energy, which results in:
Higher efficiency (often above 85%)
Compact size and lighter weight
Versatility across input voltages
Unlike linear power supplies, which dissipate excess voltage as heat, SMPS uses pulse-width modulation to regulate output, dramatically increasing efficiency and making it a favorite for both industrial and commercial systems.
How the Conversion Process Works
AC/DC Conversion – Converts input AC voltage to DC.
Switching Regulation – A high-speed transistor chops the voltage at high frequency.
Transformer Action – The chopped signal passes through a transformer to adjust voltage levels.
Rectification & Filtering – The signal is smoothed into a stable DC output.
Thanks to these steps, SMPS units can deliver reliable power to complex systems with minimal energy waste and less thermal stress on components.
Real-World Use Case
A warehouse automation system running robotic arms and conveyor motors relies on SMPS for its modular controllers. The compact design makes them easy to integrate into control cabinets, while the high efficiency keeps heat dissipation minimal—critical in enclosed environments. Additionally, maintenance staff report fewer system reboots, largely due to the SMPS's stable voltage regulation even during power fluctuations. This reliability allows the entire workflow to run with fewer interruptions, saving hours of lost productivity each month.
Why Is SMPS Better Suited for Industrial Environments Than Traditional Power Supplies?
Size, Heat, and Flexibility
In large industrial setups, space and cooling are valuable commodities. Switched mode power supply addresses these challenges by offering:
Compact design: A 240W SMPS can be a third the size of an equivalent linear unit.
Minimal heat output: Less heat means less cooling infrastructure.
Flexible voltage input ranges: Commonly supports 85–264VAC or even 100–370VDC inputs.
This versatility makes SMPS ideal for global operations where voltage standards vary. Even in mobile or container-based systems, its reduced size and universal input capability eliminate the need for bulky transformers and location-specific rewiring.
Enhanced Durability and Safety
Industrial systems often require robust safety features. Most SMPS come with:
Overload protection
Overvoltage protection
Short-circuit handling
Built-in EMI filters
These features prevent system damage, reduce downtime, and meet various industrial safety certifications such as UL, CE, or FCC. Advanced models even offer remote fault signaling, enabling operators to catch issues before they escalate—critical in environments where unplanned stoppages translate to substantial financial loss.
Application Scenario
In food processing automation, where moisture and temperature fluctuations are constant challenges, SMPS with conformal coating and wide temperature range operation ensure reliability and hygiene compliance—something traditional units struggle with. In fact, one dairy processing facility reported a 40% reduction in maintenance calls after switching to SMPS-powered control systems, primarily due to better protection against condensation-related faults and faster system recovery during voltage dips.
How Do You Choose the Right Switching Mode Power Supply?
Key Selection Criteria
Output Voltage and Current – Match these to your system load.
Input Voltage Range – Consider global compatibility if used in multiple regions.
Mounting Type – Options include DIN rail, chassis, and panel mount.
Environment – Dust-proof, water-resistant, or high-temp-rated models for tough conditions.
Certifications – UL, CE, or RoHS for specific regulatory needs.
Choosing the right SMPS isn’t just about matching electrical specs—it’s also about aligning with your system's environment and operational demands. For instance, a plant operating in a dusty steel production zone would benefit from sealed enclosures and vibration-resistant models. In contrast, a temperature-sensitive lab may prioritize extremely tight voltage accuracy and noise suppression.
|
Selection Factor |
What to Consider |
|
Output Power (W) |
Total load with 20-30% headroom |
|
Voltage Accuracy |
Needed for sensitive electronics |
|
Efficiency (%) |
Impacts thermal design and energy costs |
|
Form Factor |
Fits cabinet or panel design |
|
Operating Temperature |
Especially critical for outdoor or remote setups |
Example Scenario
A facility integrating renewable energy sources into their production line chooses SMPS with wide input tolerance and remote sensing functions. This allows them to maintain stable performance even as voltage fluctuates with solar and wind availability. The facility manager noted that integrating load-sharing-capable SMPS units also simplified their future scalability—adding new equipment required no redesign of the power system, only plugging in additional units in parallel.
What Problems Can SMPS Help Solve in Complex Industrial Systems?
1. Power Efficiency & Energy Costs
High conversion efficiency (up to 95%) reduces electricity bills and operational costs. Less energy loss also means lower cooling costs. For facilities running 24/7, the long-term savings on both power consumption and heat management can be substantial. Moreover, SMPS units with active power factor correction (PFC) can minimize reactive power penalties from utilities.
2. Reduced System Downtime
Reliable voltage regulation ensures that sensitive equipment doesn’t shut down during minor grid fluctuations. SMPS systems often include remote diagnostics to anticipate faults. Some models even support hot-swapping, allowing damaged units to be replaced without shutting down the entire system—ideal for mission-critical operations.
3. Modular Expansion
Switching power supplies make it easier to scale systems. For example, one unit can power a small machine today and be joined with others later via parallel operation. This modularity also supports redundancy, where multiple SMPS units run together and share loads, increasing system uptime and resilience.
4. Noise Immunity
Advanced filtering reduces electromagnetic interference, crucial for medical or telecom equipment where signal clarity is vital. In high-noise industrial environments, this translates to fewer data transmission errors, cleaner sensor feedback, and smoother operation of motor drives and controllers.
Scenario in Action
A North American textile mill recently upgraded from outdated power converters to modern SMPS units. Not only did machine failure rates drop by 30%, but the factory also saved thousands in electricity costs during the first year. Additionally, equipment like PLCs and HMIs experienced fewer restarts, and operators noted a more stable and responsive system—particularly during peak production hours when voltage supply can fluctuate.
Are There Any Limitations or Challenges with SMPS?
While SMPS is widely favored, it’s not without trade-offs:
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) – High-frequency switching can produce EMI, though most industrial-grade units include EMI suppression.
Complex Repair – Due to the high-density internal layout, repairs typically require replacement rather than component-level fixes.
Inrush Current – Some units can cause initial surge; mitigation requires inrush current limiters or soft-start circuits.
Additionally, for environments with strict electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements—such as medical labs or radio-sensitive areas—extra shielding or isolation may be necessary. Design engineers often pair SMPS with EMI filters, ferrite beads, or shielding enclosures to reduce emissions. It’s also worth noting that very cheap SMPS units, often without proper certifications, may suffer from ripple noise or output instability over time.
That said, in most industrial and commercial use cases, the advantages outweigh the downsides—especially when carefully matched to the right application. As long as procurement teams avoid low-grade imports and work with reputable manufacturers, the reliability of SMPS remains among the highest in its class.
Final Thoughts: Is It Time to Upgrade to SMPS?
If your operations involve sensitive electronics, require stable power, or operate in space-constrained environments, switch mode power supply offers a compelling value proposition. From lowering energy consumption to enhancing system longevity and reliability, switching mode power supplies are not just an upgrade—they’re often a necessity for modern industrial systems.
In today's increasingly automated and interconnected industries, power stability and modularity are essential. SMPS units help companies stay competitive by reducing downtime, improving energy efficiency, and simplifying future system expansions. Whether you're planning a greenfield installation or upgrading legacy systems, investing in quality SMPS solutions is a strategic decision with measurable ROI.
When selecting a supplier, look for those with experience across multiple industries, excellent service records, and products that meet global certifications. One such trusted provider is NVVV, whose portfolio of high-performance switching mode power supplies continues to support industries ranging from smart manufacturing to renewable energy.