5 Key Questions About Switching Mode Power Supply You Can't Ignore
Modern industrial systems, automation setups, and smart infrastructures all rely on consistent and efficient power conversion. One of the most vital components enabling this is the switching mode power supply (SMPS). But not all SMPS solutions are the same. To ensure your equipment runs reliably, here are five essential questions to guide your selection.
Table of Contents
What Is a Switching Mode Power Supply and How Does It Work?
Why Should You Choose SMPS Over Traditional Linear Power Supplies?
What Are the Common Applications of Switching Mode Power Supplies?
What Are the Key Factors to Consider Before Purchasing an SMPS?
How Do You Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Compatibility?
Conclusion: Why Investing in the Right SMPS Matters
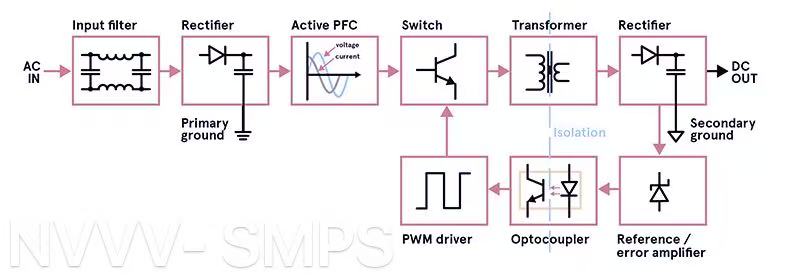
What Is a Switching Mode Power Supply and How Does It Work?
Understanding the Basics of SMPS
A switched mode power supply (SMPS) is a highly efficient electronic device that converts electrical power using a combination of high-frequency switching and energy storage components like inductors and capacitors. Unlike linear power supplies that operate by dissipating excess voltage as heat, SMPS units work by switching power transistors on and off at high speeds and controlling energy transfer through transformers or inductors.
This approach results in significant improvements in efficiency, compactness, and thermal performance, making SMPS the go-to solution for modern industrial applications where space, reliability, and energy savings are all critical.
Key Components and Function
Below is a breakdown of the essential components and their functions in a typical SMPS:
|
Component |
Function |
|
Rectifier & Filter |
Converts incoming AC power to unregulated DC. |
|
High-Frequency Switch |
Transistors switch the DC on and off rapidly to regulate energy flow. |
|
Transformer |
Provides voltage scaling and isolation between input and output circuits. |
|
Output Rectifier & Filter |
Smooths the pulsed output into stable DC suitable for sensitive electronics. |
|
Feedback Control Circuit |
Monitors output and adjusts switching to maintain voltage stability. |
High-Frequency Switching Advantage
One of the defining features of SMPS is its use of high-frequency switching, often operating between 20kHz and 2MHz. This allows for much smaller and lighter magnetic components compared to linear supplies, which use heavy transformers. High-frequency operation also enables faster response times, better voltage regulation, and the ability to integrate advanced control mechanisms like pulse-width modulation (PWM).
Why This Matters in Real Applications
Whether powering a factory's PLC system, telecom repeater station, or LED signage controller, the stable and efficient output from an SMPS ensures uninterrupted performance. The combination of reliability, reduced energy consumption, and size advantages makes it ideal for installations with tight space and high load sensitivity—characteristics frequently encountered in both Middle Eastern smart infrastructure projects and European industrial automation lines.
Why Should You Choose SMPS Over Traditional Linear Power Supplies?
Efficiency Matters
One of the most compelling reasons to choose a switching power supply over a traditional linear power supply is its superior energy efficiency. While linear power supplies typically operate at 50–60% efficiency, SMPS units can easily exceed 85–90%, even under varying load conditions. This results in reduced energy bills, less heat generation, and longer system uptime due to decreased thermal stress.
This efficiency is especially valuable in high-density installations such as server rooms, control cabinets, and automated production environments, where multiple power supplies may be operating simultaneously. In such settings, the cumulative energy savings can be substantial over time.
Space-Saving and Lightweight Design
In contrast to bulky linear power supplies that rely on large transformers and heat sinks, SMPS units are compact and lightweight, thanks to their high-frequency operation. This makes them easier to mount on DIN rails, integrate into modular systems, or use in mobile or space-constrained applications.
The following comparison table outlines the typical differences:
|
Feature |
Switching Mode Power Supply |
Linear Power Supply |
|
Efficiency |
85–95% |
50–65% |
|
Size and Weight |
Compact and lightweight |
Large and heavy |
|
Heat Dissipation |
Low |
High |
|
Output Voltage Regulation |
Excellent |
Moderate |
|
Cost (Initial) |
Slightly Higher |
Lower |
|
Long-Term Cost |
Lower due to energy savings |
Higher due to heat and power loss |
Better Handling of Voltage Fluctuations
In regions with unstable grid power—such as certain areas in the Middle East or Eastern Europe—SMPS technology offers superior tolerance to input voltage variations. Many modern SMPS units feature wide input voltage ranges (e.g., 85–264V AC), allowing them to operate reliably even when voltage dips or surges occur. This built-in flexibility protects your sensitive equipment from unexpected shutdowns or damage, ensuring operational continuity.
Lower Heat = Longer Lifespan
Less heat generation doesn't just save energy—it also reduces wear and tear on internal components. This translates to longer service life, fewer maintenance needs, and a lower total cost of ownership over time, making SMPS a sound investment for both commercial and industrial projects.
What Are the Common Applications of Switching Mode Power Supplies?
Versatility Across Industrial and Commercial Sectors
Switching mode power supplies (SMPS) are known for their broad applicability across industries that require stable and efficient DC power conversion. Whether it's an industrial robot, a data transmission station, or a compact medical diagnostic unit, SMPS units are vital for maintaining consistent performance under demanding conditions.
Industries that frequently deploy SMPS include:
Industrial Automation – to power PLCs, I/O modules, sensors, solenoid valves, and relays.
Telecommunications – for powering signal repeaters, remote terminal units (RTUs), and base stations.
Smart Buildings – in applications like access control systems, surveillance cameras, and building management systems (BMS).
LED Lighting Systems – where constant voltage or current is essential to avoid flickering and ensure energy savings.
Medical Devices – for diagnostic instruments and monitoring systems, where voltage precision and EMI shielding are critical.
Adaptable to Custom System Needs
Depending on your system architecture and environment, SMPS products are available in several designs and mounting options. Below is a summary of typical form factors and their most common usage scenarios:
|
SMPS Type |
Application Context |
|
DIN Rail Mountable |
Industrial control panels, factory automation |
|
Open Frame (PCB Mount) |
Embedded systems, medical diagnostic tools |
|
Enclosed Metal Case |
Harsh environments, dust-prone workshops, outdoor units |
|
Waterproof/IP-rated |
Outdoor lighting, irrigation control, construction sites |
For systems operating in dusty, humid, or vibration-prone areas, conformal-coated and fanless designs are available to extend longevity and reliability.
Powering the Digital Infrastructure
As digitization accelerates across Europe and the Middle East, many infrastructures—from logistics hubs to smart traffic systems—depend on reliable power conversion. SMPS plays a key role by enabling low voltage operation of sensors, controllers, and communication modules that form the backbone of these intelligent systems.
Consistency Is Key
In applications where even brief power fluctuations can cause costly downtime—such as automated production lines or remote telecom installations—SMPS delivers unmatched consistency. Their ability to maintain a regulated output even under unstable input conditions or fluctuating loads is why they are the preferred choice in mission-critical systems.
What Are the Key Factors to Consider Before Purchasing an SMPS?
Input and Output Requirements
Before selecting a switching mode power supply, the first and foremost step is understanding your input power source and required output specifications. Most industrial SMPS models accept wide-range AC inputs (e.g., 85–264V AC) or DC inputs (e.g., 110–370V DC), making them suitable for global deployments. For output, commonly used voltages include 5V, 12V, 24V, and 48V DC, depending on your equipment needs.
Ensure the SMPS can consistently deliver the rated current even during peak load demands. Undersized models may cause voltage drops or thermal shutdowns during high demand periods, while oversized models may lead to unnecessary costs and wasted space.
Voltage Stability and Ripple Control
High-quality SMPS should provide tight load regulation (e.g., ±1%) and low ripple/noise output, especially for sensitive electronic components. Excessive ripple can cause malfunctions in digital systems, communication failures in modems, or flicker in LED drivers.
Here's how to compare key electrical performance indicators:
|
Specification |
Ideal Value |
Why It Matters |
|
Load Regulation |
±0.5% to ±1% |
Ensures stable output under variable loads |
|
Line Regulation |
±0.2% to ±0.5% |
Maintains output even with input fluctuations |
|
Output Ripple & Noise |
<50mV for low-voltage models |
Prevents interference with sensitive devices |
|
Hold-up Time |
>10ms |
Allows system to ride through brief input power interruptions |
Thermal Management and Cooling Mechanisms
Depending on the power rating and environmental conditions, SMPS models may feature natural convection cooling (fanless) or active cooling (fan-equipped). Fanless models are ideal for clean, quiet, or maintenance-free applications, while fan-cooled models offer better heat dissipation under continuous high loads.
Additionally, always consider the ambient temperature range, especially in Middle Eastern or industrial factory environments where 40°C or higher is common.
Built-in Protection Features
To safeguard your devices and ensure safety, SMPS units should include:
Overvoltage Protection (OVP): Prevents damage from voltage spikes.
Overcurrent Protection (OCP): Shuts down the system in case of excess load.
Short-Circuit Protection (SCP): Avoids permanent damage during wiring failures.
Thermal Shutdown: Automatically disables the unit if it overheats.
These features are essential in environments with varying loads or power inconsistencies.
Form Factor and Installation Compatibility
Finally, ensure the form factor matches your installation setup:
DIN rail mount for industrial panels.
Wall-mounted or desktop units for laboratories or small workshops.
PCB or open-frame for OEM system integration.
Taking time to match the mechanical and electrical requirements will significantly reduce compatibility issues during commissioning.
How Do You Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Compatibility?
Focus on Quality and Component Durability
When investing in a switch mode power supply, long-term reliability is just as important as initial performance. Industrial and commercial systems often run continuously for thousands of hours. A failure in the power supply can lead to costly downtime or even damage to connected equipment.
To ensure longevity, opt for SMPS units made with high-quality capacitors, robust transformers, and PCB designs that are resistant to vibration, dust, and humidity. Look for products that advertise long Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)—ideally above 100,000 hours at 25°C ambient temperature.
Certifications and Compliance Standards
Reputable manufacturers will ensure their SMPS products comply with international safety and electromagnetic compatibility standards. Common certifications include:
|
Certification |
Purpose |
Region |
|
CE |
Safety and electromagnetic compatibility |
Europe |
|
RoHS |
Restriction of hazardous substances |
Global |
|
UL / cUL |
Product safety and fire resistance |
North America |
|
CB Scheme |
International product compliance |
Global |
Although certification may not always be mandatory, choosing certified units demonstrates a commitment to design consistency, safety, and performance reliability, especially for integration into regulated industries like telecom, medical, or industrial control systems.
Environmental and Operating Conditions
Different environments place different demands on SMPS units. In desert climates like Saudi Arabia or UAE, ambient temperatures often exceed 50°C. In contrast, Northern Europe might require performance in cold or damp environments.
To ensure compatibility:
Choose SMPS with wide operating temperature ranges, e.g., –25°C to +70°C.
For high-dust or high-humidity areas, select units with conformal coating on PCBs or IP-rated enclosures.
For mobile or high-vibration equipment (e.g., automated conveyors), seek shock and vibration-tested designs.
EMI and System Interference Considerations
Modern equipment often shares enclosures or panels with other electronics. A poorly filtered SMPS can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI) that disrupts neighboring devices such as sensors, microcontrollers, or network modules. To prevent this:
Choose power supplies that meet EMC Class B (for residential) or Class A (for industrial) emissions limits.
Ensure the manufacturer provides EMI test reports or filtering circuitry within the unit.
Choosing a Trusted Brand
Finally, selecting an experienced manufacturer can significantly affect long-term satisfaction. Look for:
Proven track record in your specific industry
Access to technical support and documentation
Availability of spare parts and replacement units
Responsive after-sales service and warranty policies
Reliable brands such as NVVV offer a full range of switching mode power supply products with high MTBF ratings, comprehensive protection features, and region-specific certifications—ensuring they can meet your operational needs today and scale with you in the future.
Conclusion: Why Investing in the Right SMPS Matters
Choosing the right switching mode power supply is not just a technical decision—it's a strategic one. A well-selected SMPS ensures long-term energy efficiency, system stability, and minimal maintenance, all of which contribute to lower operational costs and better system performance.
From understanding voltage regulation to matching environmental requirements, asking the right questions during selection can prevent costly errors down the line. Whether you're powering a factory automation system in Germany or installing an access control panel in Dubai, the right SMPS can make all the difference.
If you're looking for high-efficiency, durable, and field-proven SMPS solutions, brands like NVVV offer a wide selection of products tailored for industrial and commercial environments, backed by technical support and regional certifications.